The truth about adult cavities
What causes them and how to prevent them

Summary:
If you notice issues like swollen and painful gums, loose fillings or increased tooth sensitivity, you should consult a dentist to prevent possible damage or the loss of your teeth. Schedule dental exams for preventive care, and don’t put off additional visits to the dentist if you notice any changes to your oral health.
Most Americans don’t make it into adulthood without at least a few cavities. In fact, more than 90% of adults over the age of 40 have had tooth decay in their permanent teeth. Unfortunately, the risk of tooth decay isn’t something you can outgrow. Changes associated with aging mean that even adults can find themselves with cavities.
What causes cavities in adults?
The main culprits behind adult cavities are receding gums and failed fillings.
Receding gums
Whether due to gum disease or to overly vigorous tooth brushing, your gum tissue can become swollen or damaged, which may expose your tooth roots. Unlike the surfaces above the gum line, roots aren’t protected by hard enamel and are instead covered by a softer material known as cementum. This makes root surfaces more susceptible to plaque and decay.
If your gums have started to recede, maintaining proper daily oral hygiene is especially important. Brush gently, paying special attention to your gum line, and floss every day.
If your gum disease is severe, you may benefit from periodontal treatments, such as scaling and root planing. Your dentist can determine whether these treatments are right for you.
Failed fillings
Fillings may also be the site of adult cavities. As a filling weakens, it often fractures and the seal between the filling material and the tooth loosens. Bacteria can accumulate in the cracks and crevices, causing acid buildup that promotes decay.
Maintain your fillings to protect your teeth from further decay. Visit your dentist for regular exams. With the help of dental x-rays, your dentist can check your fillings for wear to determine whether any need to be replaced. If a filling fails and the tooth becomes decayed, it may require a root canal and crown.
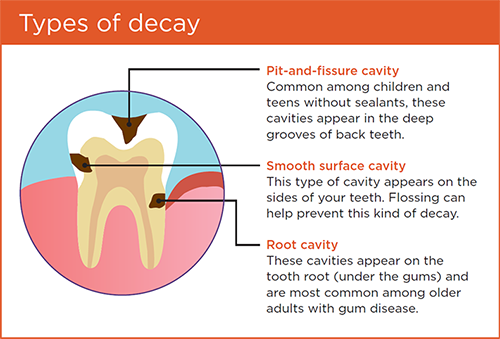
What types of cavities are there?
Tooth decay falls into three categories:
- Pit-and-fissure cavities appear in the deep grooves (also known as pits and fissures) of back teeth. Sealants are a good preventive measure for this type of decay. These cavities are most common among children and teenagers.
- Smooth surface cavities occur on the sides of your teeth. To avoid this kind of cavity, floss every day!
- Root cavities develop under the gums, on the root of the tooth. Linked to gum disease, this type of cavity generally affects older adults.
How can I avoid cavities?
Follow these tips to prevent tooth decay:
- Brush your teeth morning and night using a fluoride toothpaste. Fluoride strengthens your enamel to help prevent cavities.
- Floss between your teeth every day. Using floss regularly can interrupt the growth of cavity-causing bacteria and fight gum disease.
- Avoid starchy and sugary snacks. These types of foods encourage the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Watch out for dry mouth. Your saliva helps to both keep your teeth clean and fight cavity-causing bacteria, so drink plenty of water and let your dentist know if you’ve been experiencing dry mouth.
- Ask your dentist about supplemental fluoride (such as a fluoride rinse) to keep your teeth strong.
- Visit your dentist regularly for cleanings and exams.
Last updated July 21, 2021
Related articles:
The oral health information on this website is intended for educational purposes only. Always consult a licensed dentist or other qualified health care professional for any questions concerning your oral health.